The TA - Further Reading says "TA can be safely lowered as far as 50ppm" but I'm not seeing any description of what could happen if TA is maintained at a lower level. I had a pool installed this summer and initially I was constantly having to use acid to bring my pH down when I had TA levels of 70+. As my TA has dropped lower, I've had to use less acid as expected. More recently, my TA recently dropped down below 50 and it's now been over a month since I've had to add acid which has been nice. So I'd like to try to keep my TA down around 40 if it won't cause problems. What negative effects could I see if I keep my TA lower than 50?
Why is low TA bad?
- Thread starter falcor
- Start date
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
- May 3, 2014
- 62,672
- Pool Size
- 6000
- Surface
- Fiberglass
- Chlorine
- Salt Water Generator
- SWG Type
- Pentair Intellichlor IC-40
Welcome to the forum.
Once you are below a TA of 50 and normal CYA levels, your pH can become unstable and drop rapidly.
But if it works for you -- all is good.
Once you are below a TA of 50 and normal CYA levels, your pH can become unstable and drop rapidly.
But if it works for you -- all is good.
- Jul 21, 2013
- 65,062
- Pool Size
- 35000
- Surface
- Plaster
- Chlorine
- Salt Water Generator
- SWG Type
- Pentair Intellichlor IC-60
Watch your pH and TA carefully after any acid additions with your TA at 40 as your pH can drop over a cliff.
OK, I still haven't needed to add acid but will only add a small amount when the need does arise and retest before adding more to make sure I don't undershoot my target pH.
- Jun 24, 2021
- 15,880
- Pool Size
- 29000
- Surface
- Vinyl
- Chlorine
- Salt Water Generator
- SWG Type
- CircuPool RJ-60 Plus
What pH are you trying to target? When your TA is 50-80, pH should be fairly stable around 7.8-8.0. If, when you get to 50-60, and are trying to lower pH below about 7.8, you will get into the cycle you are describing.OK, I still haven't needed to add acid but will only add a small amount when the need does arise and retest before adding more to make sure I don't undershoot my target pH.
Leave your pH alone if it is between 7.8 and 8.0. When it gets above 8, only lower to 7.8 or 7.9 and you should be fine.
The TA can be very low with a pH in the 7 to 8 range.
For example, if you have distilled water, you can have a pH of 7 with no bicarbonate or carbonate alkalinity.
The only alkalinity you will have is enough hydroxide to make the pH 7 vs. 4.5.
At a pH of 7.0, the TA from hydroxide is 0.0000001 moles per liter or about 40 grams in 10,000,000 liters, which is about 0.005 ppm TA.
At a pH of 8.0, the TA from hydroxide is 0.000001 moles per liter or about 40 grams in 1,000,000 liters, which is about 0.05 ppm TA.
For water exposed to air, you will have carbon dioxide in the water, which will turn into bicarbonate and carbonate.
So, the TA at pH levels in the 7 to 8 range will never be below 1.0.
For Carbonate alkalinity, the bicarbonate is in equilibrium with carbon dioxide based on the pH.
Once the pH is below 6.35, carbon dioxide is more than 50% by molar ratio.
X = pH.
Y = %.
The Blue Line is the percentage bicarbonate.
The Yellow Line is the percentage Carbon Dioxide.
HCO3- + H+<--> H2O + CO2aq
 www.wolframalpha.com
www.wolframalpha.com

If you keep the TA very low, you also have to calculate the carbonate alkalinity by subtracting the cyanurate and borate alkalinity.
You can use PoolMath to monitor CSI to keep it in a good range.
Get PoolMath and keep the CSI in the -0.3 range for the heater and for the fiberglass warranty even though fiberglass and copper should not need CSI.
Heaters are most at risk from low pH, so you have to be extra careful to never allow the pH to crash even for a brief period of time.
So, you can go lower than 50, but it requires special attention to several issues that can become a problem.
You have less buffer, so you get more movement from added acid, so you have to be extra careful not to add too much acid and drop the pH below 7.2.
Borate C.F (correction factor) based on pH.
pH.......CF
7.2.....0.051
7.4.......0.0786
7.6......0.1248
7.8......0.1989
Cyanuric Acid correction factor based on pH.
pH........CF
7.0.......0.22
7.1.......0.24
7.2.......0.26
7.3.......0.28
7.4.......0.30
7.5.......0.32
7.6.......0.33
7.7.......0.34
7.8.......0.35
7.9.......0.36
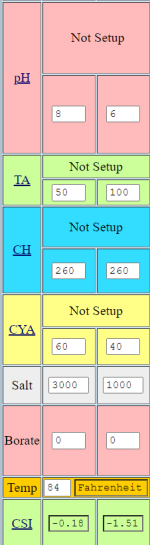
For example, if the pH = 7.6, TA = 90, Borate = 50 and CYA = 70, the adjusted alkalinity is 90 - (70 x 0.33) – (50 x 0.1248) = 60.66.

Pool Care Basics
Overnight Chlorine Loss Test
SLAM Process
PoolMath
FC/CYA Levels
Test Kits Compared
For example, if you have distilled water, you can have a pH of 7 with no bicarbonate or carbonate alkalinity.
The only alkalinity you will have is enough hydroxide to make the pH 7 vs. 4.5.
At a pH of 7.0, the TA from hydroxide is 0.0000001 moles per liter or about 40 grams in 10,000,000 liters, which is about 0.005 ppm TA.
At a pH of 8.0, the TA from hydroxide is 0.000001 moles per liter or about 40 grams in 1,000,000 liters, which is about 0.05 ppm TA.
For water exposed to air, you will have carbon dioxide in the water, which will turn into bicarbonate and carbonate.
So, the TA at pH levels in the 7 to 8 range will never be below 1.0.
For Carbonate alkalinity, the bicarbonate is in equilibrium with carbon dioxide based on the pH.
Once the pH is below 6.35, carbon dioxide is more than 50% by molar ratio.
X = pH.
Y = %.
The Blue Line is the percentage bicarbonate.
The Yellow Line is the percentage Carbon Dioxide.
HCO3- + H+<--> H2O + CO2aq
y = (100/(1+10^(6.35– x))) and y = 100 - (100/(1+10^(6.35– x))), x from 4. to 8. - Wolfram|Alpha
Wolfram|Alpha brings expert-level knowledge and capabilities to the broadest possible range of people—spanning all professions and education levels.

If you keep the TA very low, you also have to calculate the carbonate alkalinity by subtracting the cyanurate and borate alkalinity.
You can use PoolMath to monitor CSI to keep it in a good range.
Get PoolMath and keep the CSI in the -0.3 range for the heater and for the fiberglass warranty even though fiberglass and copper should not need CSI.
Heaters are most at risk from low pH, so you have to be extra careful to never allow the pH to crash even for a brief period of time.
So, you can go lower than 50, but it requires special attention to several issues that can become a problem.
You have less buffer, so you get more movement from added acid, so you have to be extra careful not to add too much acid and drop the pH below 7.2.
Borates and Adjusted Alkalinity.
Adjusted TA = TA – (CYA X CYA C.F) – (Borate x Borate CF)Borate C.F (correction factor) based on pH.
pH.......CF
7.2.....0.051
7.4.......0.0786
7.6......0.1248
7.8......0.1989
Cyanuric Acid correction factor based on pH.
pH........CF
7.0.......0.22
7.1.......0.24
7.2.......0.26
7.3.......0.28
7.4.......0.30
7.5.......0.32
7.6.......0.33
7.7.......0.34
7.8.......0.35
7.9.......0.36
For example, if the pH = 7.6, TA = 90, Borate = 50 and CYA = 70, the adjusted alkalinity is 90 - (70 x 0.33) – (50 x 0.1248) = 60.66.

Pool Care Basics
Overnight Chlorine Loss Test
SLAM Process
PoolMath
FC/CYA Levels
Test Kits Compared
Last edited:
Heaters form a patina of copper oxide, copper hydroxide, copper carbonate, calcium carbonate etc. as the copper gets oxidized and the patina should protect the elemental copper from further oxidation.
At low pH, the patina will not form or if there is a patina, it will be stripped off pretty fast.
So, CSI is only slightly relevant.
High CSI can cause scaling and low CSI might increase corrosion, but pH is more important than CSI.
For fiberglass, the manufacturer will usually require specific levels for everything.
CSI might have some small effect, but probably not a lot of effect.
Low TA means low carbonate, which means low CSI because CSI is a combination of calcium ion levels and carbonate ion levels.

At low pH, the patina will not form or if there is a patina, it will be stripped off pretty fast.
So, CSI is only slightly relevant.
High CSI can cause scaling and low CSI might increase corrosion, but pH is more important than CSI.
For fiberglass, the manufacturer will usually require specific levels for everything.
CSI might have some small effect, but probably not a lot of effect.
Low TA means low carbonate, which means low CSI because CSI is a combination of calcium ion levels and carbonate ion levels.

With a TA of 1, you would use 0.9 oz of acid to lower the pH from 8 to 7.8 and 4 oz would drop the TA to 0 and the pH to 4.5.
With a TA of 100, you would use 9.6 oz of acid to lower the pH from 8 to 7.8.
With a TA of 10, 40 oz would drop the pH from 8 to 4.5 (If the TA = 0, then the pH will be 4.5).



With a TA of 100, you would use 9.6 oz of acid to lower the pH from 8 to 7.8.
With a TA of 10, 40 oz would drop the pH from 8 to 4.5 (If the TA = 0, then the pH will be 4.5).



Last edited:
Thread Status
Hello , This thread has been inactive for over 60 days. New postings here are unlikely to be seen or responded to by other members. For better visibility, consider Starting A New Thread.