Black stains on a metal pool light, appearing when there is copper in the pool water, are likely caused by copper oxide buildup which can form dark, blackish stains on metal surfaces, especially when the pool's pH is not properly balanced, allowing copper ions to precipitate out and settle on the light fixture.
Light's Chrome Finish Lost
- Thread starter cwilliamp
- Start date
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Mystery Stains in Salt Generator Pools
Salt chlorine pools are quite popular for their convenience, but some homeowners and service pros report discolored water and strange stains that accompany them. Where do these stains come from?
The electrolysis still points to an electrical issue.
Electrons can flow towards the light or away from the light depending on the circumstances.
If electrons are going away from the light, the light will corrode (Light is the anode).
If electrons are moving towards the light, you can get plating of other metals like copper, silver etc. (Light is the Cathode).
The copper gets reduced from Cu2+ ions to Copper metal.
You can also get other metals and probably ionic compounds like copper oxide, which is black.
Electrons go from the negative terminal of a battery to the positive terminal.
Note: Technically "current" flows from the positive terminal to the negative terminal because "Current" is defined as the flow of positive charge.
Cu2++ 2e- → Cu (cathode).
Cathode reaction (reduction):
At the cathode (the surface to be plated), the copper ions from the solution gain electrons and deposit as solid metallic copper on the surface.
A positive standard reduction potential indicates that a substance has a greater tendency to be reduced, meaning it readily gains electrons and acts as a stronger oxidizing agent; the more positive the value, the higher the likelihood of reduction occurring.
A negative standard reduction potential indicates that a substance has a greater tendency to be oxidized rather than reduced, meaning it is more likely to lose electrons and act as a reducing agent compared to a substance with a positive potential; essentially, the more negative the value, the stronger the reducing agent it is.


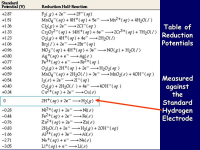
Copper oxide refers to a chemical compound composed of copper and oxygen, most commonly either copper(II) oxide (CuO), also known as cupric oxide, or copper(I) oxide (Cu2O), also called cuprous oxide; both are inorganic compounds with different oxidation states of copper.
Chemical formulas: CuO (copper(II) oxide), Cu2O (copper(I) oxide).
Appearance: Copper(II) oxide is typically black powder, while copper(I) oxide can appear red or yellow depending on particle size.

Copper(I) oxide or cuprous oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Cu2O.
Electrons can flow towards the light or away from the light depending on the circumstances.
If electrons are going away from the light, the light will corrode (Light is the anode).
If electrons are moving towards the light, you can get plating of other metals like copper, silver etc. (Light is the Cathode).
The copper gets reduced from Cu2+ ions to Copper metal.
You can also get other metals and probably ionic compounds like copper oxide, which is black.
Electrons go from the negative terminal of a battery to the positive terminal.
Note: Technically "current" flows from the positive terminal to the negative terminal because "Current" is defined as the flow of positive charge.
Cu2++ 2e- → Cu (cathode).
Cathode reaction (reduction):
At the cathode (the surface to be plated), the copper ions from the solution gain electrons and deposit as solid metallic copper on the surface.
A positive standard reduction potential indicates that a substance has a greater tendency to be reduced, meaning it readily gains electrons and acts as a stronger oxidizing agent; the more positive the value, the higher the likelihood of reduction occurring.
A negative standard reduction potential indicates that a substance has a greater tendency to be oxidized rather than reduced, meaning it is more likely to lose electrons and act as a reducing agent compared to a substance with a positive potential; essentially, the more negative the value, the stronger the reducing agent it is.



Copper oxide refers to a chemical compound composed of copper and oxygen, most commonly either copper(II) oxide (CuO), also known as cupric oxide, or copper(I) oxide (Cu2O), also called cuprous oxide; both are inorganic compounds with different oxidation states of copper.
Chemical formulas: CuO (copper(II) oxide), Cu2O (copper(I) oxide).
Appearance: Copper(II) oxide is typically black powder, while copper(I) oxide can appear red or yellow depending on particle size.

Copper(I) oxide or cuprous oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula Cu2O.
Last edited:
Since it appears that the light is the cathode, the light should be protected from corrosion, which is good except for the discoloration.
The source of the electrons is a different issue, which might or might not indicate a problem.
Most likely a stray current.
Since the electrons seem to have a preferred direction, it would indicate a possible DC voltage.
A full bonding grid would be advisable if it can be done.
The source of the electrons is a different issue, which might or might not indicate a problem.
Most likely a stray current.
Since the electrons seem to have a preferred direction, it would indicate a possible DC voltage.
A full bonding grid would be advisable if it can be done.
Thank you for all the information. Unfortunately, most of it goes over my head.
I don't understand this "stray current" idea.
Does this stray current exist only when the pool pump is powered, or light is powered?
Should I be able to measure this stray current between the light ring and something else? What could that something else be?
What in this pool could generate DC voltage?
Regarding copper in the water. Last spring I had a mustard algae bloom and I used Swimtrine Plus algacide. It has Copper Ethanolanine Complex 28.94%, Metalic Copper Equivalent of 9.3%, and 0.97 lbs of elemental copper per 1 gallon. I suspect this is the source of the copper. Also, on January 30, a pool supply company test of my water showed 0.2 ppm iron and 0.1 ppm of copper.
I don't understand this "stray current" idea.
Does this stray current exist only when the pool pump is powered, or light is powered?
Should I be able to measure this stray current between the light ring and something else? What could that something else be?
What in this pool could generate DC voltage?
Regarding copper in the water. Last spring I had a mustard algae bloom and I used Swimtrine Plus algacide. It has Copper Ethanolanine Complex 28.94%, Metalic Copper Equivalent of 9.3%, and 0.97 lbs of elemental copper per 1 gallon. I suspect this is the source of the copper. Also, on January 30, a pool supply company test of my water showed 0.2 ppm iron and 0.1 ppm of copper.
Most pools have some amount of voltage and current due to all of the electricity we use in modern life.
There are many sources of current and voltage like neutrals tied to ground, power lines underground possibly being in contact with the earth due to defects in the wiring, cable tv wires, telephone, internet etc.
There are many sources of current and voltage like neutrals tied to ground, power lines underground possibly being in contact with the earth due to defects in the wiring, cable tv wires, telephone, internet etc.
Last edited:
Current moving through wires near the pool will create electromagnetic fields that can induce current in nearby conductors.
There might be zinc, magnesium, aluminum etc. somewhere that can push electrons to everything that is electrically connected to the light.
Metals like zinc are anodes and they are eager to lose electrons like the negative terminal of a battery.
These electrons are received by the copper and the copper is converted from ions to elemental metal.
Basically, the light has an excess of electrons with enough voltage to reduce copper ions into copper metal as the copper ions make contact with the light.
There might be zinc, magnesium, aluminum etc. somewhere that can push electrons to everything that is electrically connected to the light.
Metals like zinc are anodes and they are eager to lose electrons like the negative terminal of a battery.
These electrons are received by the copper and the copper is converted from ions to elemental metal.
Basically, the light has an excess of electrons with enough voltage to reduce copper ions into copper metal as the copper ions make contact with the light.
Last edited:
Once the copper has been electroplated onto the stainless steel, it can probably be oxidized by chlorine or oxygen into CuO copper(II) oxide) and Cu2O (copper(I) oxide).
The light is acting like it has either an anode attached or some sort of Impressed Current Cathodic Protection.
This will reduce the oxidation of copper, but it probably won't stop all copper oxidation.
The voltage being impressed onto the light might not be consistent.
The source of voltage might be an anode metal like aluminum, zinc or magnesium or it might be a DC power source.

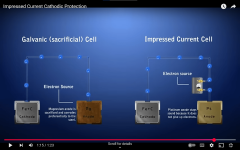
The light is acting like it has either an anode attached or some sort of Impressed Current Cathodic Protection.
This will reduce the oxidation of copper, but it probably won't stop all copper oxidation.
The voltage being impressed onto the light might not be consistent.
The source of voltage might be an anode metal like aluminum, zinc or magnesium or it might be a DC power source.


Things that make contact with the Cathode (Light) can be reduced (Gain Electrons).
Any anode metal (Zinc, magnesium etc.) will corrode.
If the voltage is due to a DC power source, then that provides the impressed current.
Reduction can be chlorine to chloride, oxygen to oxide, Copper ions to copper metal, hydrogen to hydrogen gas etc.

Any anode metal (Zinc, magnesium etc.) will corrode.
If the voltage is due to a DC power source, then that provides the impressed current.
Reduction can be chlorine to chloride, oxygen to oxide, Copper ions to copper metal, hydrogen to hydrogen gas etc.

AC can be rectified to DC under some circumstances.
Trying to measure voltage in these cases is difficult.
The hard part is finding a good reference point to measure against.
If you can test for voltage, test for frequency to see if the voltage is a common 60 Hz signal or a DC signal.
The power lines near the property are a possible source of stray current.
Maybe have an electrician check everything to see if it is all safe.
Trying to measure voltage in these cases is difficult.
The hard part is finding a good reference point to measure against.
If you can test for voltage, test for frequency to see if the voltage is a common 60 Hz signal or a DC signal.
The power lines near the property are a possible source of stray current.
Maybe have an electrician check everything to see if it is all safe.
Thread Status
Hello , This thread has been inactive for over 60 days. New postings here are unlikely to be seen or responded to by other members. For better visibility, consider Starting A New Thread.




