@Leebo I know that Ascorbic Acid affects PH/Alkalinity, but I'm never sure how much it lowers PH/Alk,
Can this be added to the PoolMath app?
Can this be added to the PoolMath app?
Last edited:
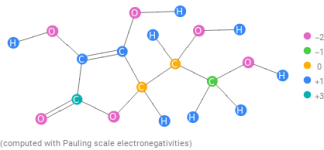
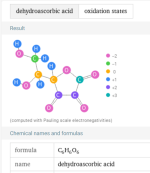
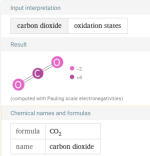
That is the total drop with the breakdown of the dehydroascorbic acid, but we do not know how long that takes.So 3lbs of Ascorbic Acid would drop TA by 28.5 ppm? @JamesW
I'm going to do a treatment in the fall, 2 weeks before I close and report back on initial TA loss, TA after 24 hours, TA when starting to add Chlorine, and TA once Chlorine starts to hold.Excellent analysis.
Unfortunately this would not be easy to add to pool math as there are too many unknowns around how the acidic chlorine reactions would happen. I suppose one could put in a simple estimate of the effect with some strong warnings about what to expect. AA treatments are not universally used by most pool owners (I’ve never had to use it), so it has a limited audience.
 [/sup][/sup]
[/sup][/sup]
